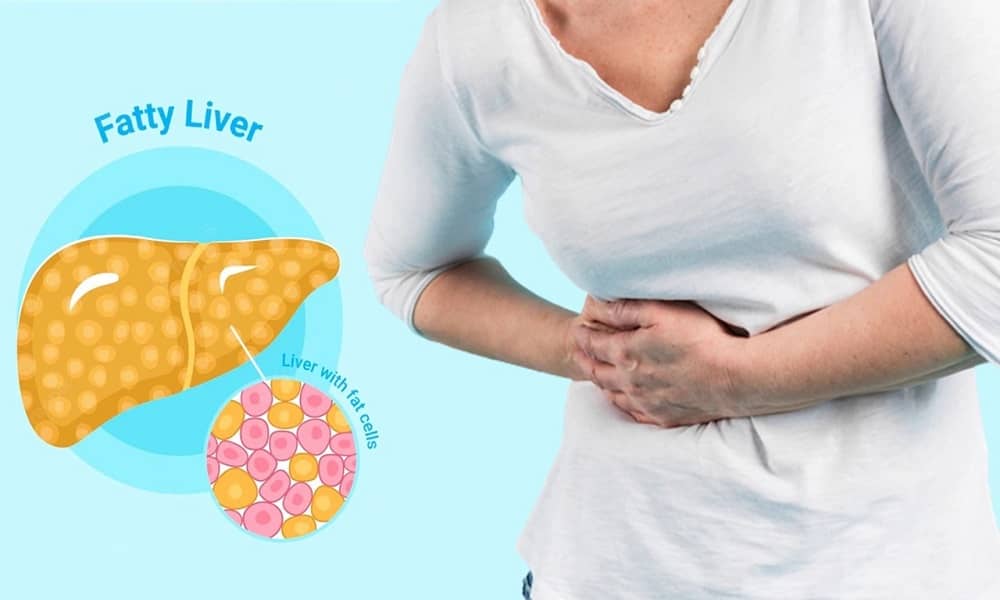

03 Mar 6 Most Common Causes of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) suggests excess deposition of fat in the liver but not because of alcohol.
NAFLD has mainly four stages:
- Simple fatty liver
- Non-alcoholic
- Fibrosis
- Cirrhosis
Initially, when the disease is at its primary stage, it does not cause any harm but at later stages of cirrhosis, the liver becomes permanently dysfunctional.
Since there isn’t any old or new treatment for fatty liver disease promising a permanent cure, it’s best to prevent it from worsening.
With the correct diet and lifestyle, you can still prevent your fatty liver from worsening and can even reduce the amount of fat deposited.
However, the first step of understanding any disease is understanding its root causes, which often helps prevent the disease.
What Causes Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)?
The pathology of fatty liver involves:
- Synthesis of fatty acids in liver cells
- Accumulation of lipids because of impaired beta-oxidation
- Retention of lipids because of less secretion of hepatocytes apolipoprotein
Moreover, there can be some common and other uncommon causes that alter the regular functioning of the liver cells and lead to the above pathology.
What Causes NAFLD – 6 Most Common Reasons for Fatty Liver
So, what causes a fatty liver other than alcohol?
Essentially, there are six main factors that highly put you at risk of getting non-alcoholic fatty liver:
- Hypertension/high blood pressure
- Obesity
- Type II Diabetes
- Metabolic Syndrome
- Cholesterol
- Insulin Resistance
All these reasons for NAFLD are explained right below in more detail…
#1. High Blood Pressure
Hypertension is associated with metabolic syndrome which includes insulin resistance.
Since insulin resistance increases the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver, hypertension can pave the way for the development of the disorder.
Though hypertension in most of the cases is responsible for fatty liver among the obese population, recent cases of non-obese patients have also emerged.
According to a report, people with hypertension had higher insulin resistance with higher levels of insulin in the plasma.
#2. Obesity
Obesity characterizes a person with a lot of bodyweight and is a common problem.
Its association with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is similar to hypertension as excess fat increases insulin resistance.
This further increases inflammatory response from the liver cells themselves leading to the accumulation of more fat in the liver.
Also, one of the main causes of obesity is overeating, which causes excess calorie intake which can further deposit in the liver.
#3. Type II Diabetes Mellitus
A common condition among the population these days, type II diabetes mellitus causes the levels of sugar or glucose to increase in the blood.
The relationship between diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is bidirectional where diabetes worsens and aggravates the latter.
In fact, it can lead to the progression of stage one non-alcoholic fatty liver disease to NASH (Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis), while NAFLD can increase the risk of a person developing diabetes.
But in the end, it’s Diabetes II that causes nash.
#4. Metabolic Syndrome
The term combines diabetes, hypertension, and obesity.
Hence, a person suffering from all these three is said to be suffering from metabolic syndrome.
While it already puts you at risk of many heart diseases, it can also lead to cirrhosis, which is a complication of NAFLD.
Some of its common symptoms include:
- High cholesterol
- Insulin resistance
- Hypertension where your systolic pressure is 140 and diastolic at 90 constantly.
#5. High Cholesterol
Constant high cholesterol levels in your blood can lead to the accumulation of hepatic free cholesterol, causing progression in the pathogenesis of NAFLD.
This accumulation can also damage the hepatic cells.
SUGGESTED READ: Foods to Lower LDL and Raise HDL Cholesterol
#6. Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance initiates a constant inflammatory response from the cells of your liver, damaging the cells and leading to fatty liver disease.
Though these are the risk factors of NAFLD, taking the right medications for the above medical conditions can prevent its development.
Other than these factors, there are secondary causes of NAFLD too which are uncommon and yet contribute to its development.
What Can Cause Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease – Uncommon Factors
Apart from some of the common reasons for fatty liver mentioned above, we also have some uncommon causes at hand.
#1. Lipid Metabolic Disorders
Many lipid metabolism disorders can cause fatty liver diseases, including:
- Abetalipoproteinemia – It is caused by a mutation in the gene required for the metabolism of triglycerides. This results in the accumulation of triglycerides in the liver cells.
- Hypobetalipoproteinemia – It is a genetic disease caused by a mutation in the gene characterized by low levels of low-density lipids. This can cause the excess synthesis of VLDL (very-low-density lipoprotein) that leads to the accumulation of triglycerides in the cells of the liver.
#2. Nutritional Causes
- Intravenous glucose – Long-term administration of intravenous glucose or calories can cause a reduction in the carnitine levels, which is a compound that takes out free fatty acids from the liver. As the carnitine levels deplete, the transfer of free fatty acids from the cytoplasm of the liver will be reduced.
- Surgical weight loss – Some people often go for surgical procedures to lose weight. But that destroys your liver cells leading to the development of NAFLD and further NASH.
- Starvation – It could be due to dieting purposes or due to disorders, but ultimately reduces the protein levels leading to a decrease in VLDL and diminished transport. This can cause the accumulation of lipids in the liver.
#3.Medications
There are many medications like HAART that can follow various pathways to destroy your liver cells or cause an excess inflammatory response, leading to NAFLD and further cirrhosis.
For example, corticosteroids can inhibit the beta-oxidation of lipids causing their accumulation in the liver.
Hence, it is best to avoid taking such medications in case you are already suffering from stage one NAFLD.
Medications to avoid fatty liver disease are:
- Methotrexate
- Tamoxifen
- Amiodarone
You can also consult your doc for more information on other medications.
#4. Other Causes of Fatty Liver Disease
Certain diseases other than metabolic syndrome can also increase your risk of falling prey to fatty liver disease, including:
- Celiac diseases
- Wilson disease
- Hepatitis C virus
It’s worth mentioning that environmental factors like phosphorus poisoning too can lead to the progression of fatty liver disease.
However, these causes are usually rare and not common in the higher population suffering from the disease.
Despite all this, managing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is still possible by identifying it at the right time.
How to Know You Have NAFLD? [Symptoms]
In almost 45% to 95% of cases, non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases are asymptomatic.
Especially at the initial stages, they don’t usually show signs that can help you differentiate it from any other disease.
For example, two of the signs that were found common among patients suffering from initial stages of NAFLD were:
#1. Fatigue
The fatigue that you notice during non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is characterized by spending most of the day being inactive.
For example, excessive sleeping during the daytime. However, it doesn’t define the severity of the condition or the stage at which your NAFLD is.
#2. Pain
It is mostly felt during the later stages of the condition, usually before cirrhosis. You can experience pain around the top right area of your tummy; this could be a dull or severe pain.
At advanced stages, or stages of NASH and cirrhosis of the liver, these symptoms can worsen and a patient might experience:
- Swelling in the abdominal region – Sometimes due to failure of the liver, one can feel as if their stomach is full or is larger than it was normally. It can even be painful sometimes.
- Varicose veins – Tiny visible veins in different areas of your body could be a symptom of the non-alcoholic fatty liver caused by the accumulation of fat in the liver. The fat accumulation causes the sluggish flow of the blood impacting the blood pressure.
- Splenomegaly – According to many studies, patients suffering from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease showed signs of enlarged spleen at advanced stages.
- Palmar erythema or red palms – It can be a sign of liver disease as 23% of people suffering from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease show these signs.
- Fatty liver symptoms on the skin – Yellowness of the skin or jaundice is commonly reported during liver inflammation or enlargement due to fat accumulation.
Now, the first two steps of understanding your disease are done, next is the diet.
Since the fatty liver disease is mostly about the accumulation of excess fat in the liver, it’s important to take care of what foods you eat and what you have got to avoid.
Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Diet – What to Eat?
A customized fatty liver diet is beneficial for both alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver.
The most important part of the diet is to maintain a sustainable routine of food choices.
Here, we want to include the following important parts of a balanced diet:
- Fibers
- Vegetables and fruits
- Whole grains
Go with the following recommendations for your diet.
Foods To Add in Your Diet for Fatty Liver
According to health experts, the best way to manage and prevent your fatty liver from worsening, you should limit your calorie intake.
While the choices contain mainly portions of the Mediterranean diet, you can opt for the following foods:
#1. Low Fat Cow Milk
According to studies, taking enough vitamin D helps manage non-alcoholic fatty liver to some extent. Since we don’t wanna add up extra calories, we suggest you opt either for low-fat cow milk or almond milk.
#2. Caffeine
Coffee with no added sugar or sweeteners can help your body absorb fewer fats, preventing excess accumulation of fat in your liver. But the research on this is still going on and we need more evidence.
#3. More Vitamin E
There are many sources of Vitamin E like bell peppers or peanuts that you can add to your diet to notice improvements in the symptoms of NAFLD.
#4. Seafood
Mainly fishes like tuna and salmon contain omega 3 fatty acids that help in reducing the fat accumulated in your liver.
#5. Fibers
There are various sources of fiber that you can try to reduce triglycerides. Some good sources are whole grains like oatmeal.
#6. Nuts
According to health experts, consuming nuts helps in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress that could be responsible for NAFLD.
Apart from adding foods, you also need to subtract some foods to prevent your condition from worsening.
Foods to Avoid with Fatty Liver Disease
Since one of the most common risk factors of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is insulin resistance, it is best to avoid foods that can shoot up your glucose levels.
Hence, make sure you cut out the following foods from your non-alcoholic fatty liver disease diet:
#1. Packaged Juices: Sugars and processed carbs are highly dangerous for your liver, and, hence, experts suggest avoiding them when suffering from fatty liver.
#2. Alcohol: While it already causes alcoholic fatty liver, consuming it during non-alcoholic fatty liver can fasten its progression.
#3. Fried Foods: Now, this is not hard for you to guess! These actually contain high amounts of calories that can raise the levels of free triglycerides in your body.
#4. Salty Foods: Consuming foods high in salt can aggravate fatty liver by two pathways, first by increasing the fat levels and second by impairing the renin-angiotensin system, increasing the risk of progression of NAFLD.
#5. Fatty Meats: The first rule of not adding too many calories comes in here. Also, they are high in saturated fats that increase the risk of cirrhosis.
#6. Desserts and Cakes: Cutting these out of your diet helps cut out sugars and saturated fats as well.
Next, we talk about can fatty liver be reversed as we take on some serious discussion on its treatment and management.
Treatment of NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease)
Non-alcoholic fatty liver cannot be cured completely. Hence, the main aim of the treatment plan is to prevent fibrosis or cirrhosis of the liver.
If the liver is already fibrosed, then the treatment plan is designed to reduce it.
Although current agents used in the treatment planning aren’t much effective, the best way to treat the disease is by understanding the cause.
For example in obese patients, the first step is always reducing weight through more physical activity and exercise.
Now, while weight reduction helps prevent the progression of the disease into liver fibrosis, it doesn’t help when the liver is already fibrosed.
Pharmacologically, medications are prescribed keeping in mind the stage of insulin resistance.
Other than these possible methods, only lifestyle remedies remain to get a healthy liver.
Lifestyle Changes for Fatty Liver Disease
The following lifestyle modifications will help avoid as well as prevent the fatty liver disease from worsening.
#1. Exercises
Reducing weight can to some extent help you manage fatty liver and prevent its progression.
You can add exercises to your daily routine. Even moderate exercise helps you reduce the fat accumulated in the liver.
Try going for:
- Brisk walks
- Swimming
- Running
- Cycling
#2. Restrict Calorie Intake
The more calories you take in, the more fat levels accumulate in your body that can get settled in your liver worsening from stage I to stage II.
You can restrict calorie intake by following the above diet pattern and adding more fibers and cutting saturated carbs.
#3. Fixing Your Sleep Schedule
Sleeping at a fixed time daily helps in controlling many diseases as it improves your digestion, metabolism, and hormonal balance.
But, most importantly, it balances the hunger and satiety hormones, which is a good thing for your liver.
#4. Moderate Your Alcohol Intake
People suffering from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease should moderate their alcohol intake to prevent more accumulation of fat.
RELATED: How Does Alcohol Affect Liver
#5. Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water helps boost up your metabolism to burn more calories and maintain a good lipid and carbs profile.
Final Word
Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases are initially harmless with no symptoms that hamper your daily life.
But as it advances into the later stages, the complications become severe with even chances of developing cirrhosis.
According to reports, the nonalcoholic cirrhosis of the liver life expectancy is just 19 to 24 years, which makes it essential for people to know more about fatty liver.
While there isn’t a proper cure for the condition, making changes to the diet and your lifestyle can help prevent fibrosis and cure the disease to some extent.
In cases of stage I fatty liver, weight management and the right medications for the causative factor can help prevent liver fibrosis.
But in later cases as in the case of insulin resistance, it is always good to take medications that can be prescribed by your doctor post-diagnosis.
In any case, the right lifestyle measures will always help. Hopefully, you got something out of this blog. Do leave your feedback and queries down below.


No Comments